Discover what foods are the best for losing weight on a liquid diet foods! Follow this simple guide to make sure you’re getting all of the nutrients!
When following a liquid diet, it’s important to ensure that you’re still getting all the necessary nutrients your body needs. While it may seem challenging to find nutrient-rich options in liquid form, several choices can help you succeed on your liquid diet journey.
What is a liquid diet?
A liquid diet is a type of diet that primarily consists of liquids or foods that are in a liquid or semi-liquid state. This form of diet restricts or eliminates the consumption of solid foods, and it often involves the intake of various liquids such as soups, broths, smoothies, shakes, and juices. Liquid diets may be prescribed or followed for various reasons, and they can serve different purposes. Here are some common types of liquid diets:
- Clear Liquid Diet: This type of liquid diet allows only transparent or clear fluids. It is often used for short periods before medical procedures or surgeries. Examples include clear broth, water, tea, clear fruit juices, and popsicles.
- Full Liquid Diet: This diet includes a broader range of liquids, allowing for more nutritional variety. It may include clear liquids, as well as creamy soups, pureed vegetables, yogurt, milk, and meal replacement, shakes.
- Medically Supervised Liquid Diet: Some individuals may follow a liquid diet under medical supervision for specific health conditions or weight management. These diets are often monitored by healthcare professionals to ensure that nutritional needs are met.
- Detox or Juice Cleanse: Some people follow liquid diets for detoxification or cleansing purposes. This may involve consuming freshly squeezed fruit and vegetable juices for a limited duration.
- Protein Shake or Meal Replacement Diet: This type of liquid diet involves replacing one or more meals with protein shakes or meal replacement drinks. It is often used for weight loss or as a convenient way to meet specific nutritional goals.
Liquid diets can be beneficial for certain medical conditions, pre-surgical preparations, or short-term weight loss goals. However, they also have potential risks, including nutrient deficiencies and inadequate caloric intake if not properly balanced. It’s crucial for individuals considering a liquid diet to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to ensure that the diet meets their nutritional needs and is appropriate for their specific health goals. Long-term or extreme liquid diets without proper supervision can pose health risks and may not be sustainable over time.
Liquid Diet benefits
- Nutrient Absorption: Liquid diet foods are easily digestible, promoting efficient nutrient absorption for optimal health.
- Weight Management: Including liquid diet foods can aid in weight loss by controlling calorie intake and promoting a feeling of fullness.
- Hydration: Many liquid diet foods, such as smoothies and soups, contribute to overall hydration, supporting bodily functions.
- Digestive Rest: Liquid diets provide a break for the digestive system, allowing it to rest and potentially alleviate digestive issues.
- Detoxification: Certain liquid diet options, like detox smoothies, can assist the body in eliminating toxins and promoting a cleaner system.
- Convenience: Liquid diet foods are often convenient and time-saving, making them a practical choice for busy lifestyles.
- Improved Gut Health: Some liquid foods, such as probiotic-rich drinks, can enhance gut health by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria.
- Quick Nutrient Delivery: Liquid meals can offer a quick and efficient way to deliver essential nutrients, especially for individuals with difficulty chewing or swallowing.
- Increased Energy Levels: Properly balanced liquid diets can provide a steady source of energy, reducing energy fluctuations throughout the day.
- Medical Support: Liquid diets are sometimes recommended for medical purposes, such as pre-surgery preparation or post-operative recovery.
How liquid diet works?
A liquid diet typically involves consuming foods and beverages in a liquid or semi-liquid form, providing a source of nutrients while minimizing solid food intake. The way a liquid diet works can vary based on its purpose and the specific plan followed, but here are some general principles:
- Caloric Restriction: Liquid diets often involve a controlled reduction in calorie intake. By consuming liquids, individuals may naturally limit their overall calorie consumption, which can contribute to weight loss.
- Nutrient Density: Despite the liquid form, a well-designed liquid diet aims to provide essential nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, proteins, and carbohydrates. This ensures that the body receives the necessary elements for proper functioning.
- Digestive Rest: Liquid diets can give the digestive system a break by providing easily digestible nutrients. This may be beneficial for individuals with certain digestive issues or those preparing for medical procedures.
- Hydration: Many liquid diet foods, such as broths, soups, and smoothies, contribute to hydration. Proper hydration is crucial for various bodily functions, including metabolism and the elimination of waste.
- Weight Management: Liquid diets are often used for short-term weight management or as a jumpstart to a more sustainable long-term dietary plan. The controlled intake of calories helps create a caloric deficit, promoting weight loss.
- Medical Applications: Liquid diets may be recommended by healthcare professionals for medical reasons. For example, they are sometimes used as part of the preparation for certain medical procedures or surgeries.
- Detoxification: Some liquid diets claim to support detoxification by providing nutrient-dense liquids that support the body’s natural detox processes. However, the scientific evidence supporting the idea of “detox” diets is often limited.
- Gradual Transition: Some individuals use liquid diets as a way to transition into solid food after a period of fasting or illness. This allows the digestive system to gradually reintroduce more complex foods.
liquid diet foods
| Liquid Diet Foods | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|
| 1. Smoothies | – Provides a blend of fruits, vegetables, and proteins. |
| – High in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. | |
| 2. Soups | – Offers hydration and warmth. |
| – Can include vegetables, proteins, and grains. | |
| 3. Broths | – Low-calorie option with essential nutrients. |
| – Supports hydration and easy digestion. | |
| 4. Protein Shakes | – Convenient source of protein for muscle support. |
| – Aids in muscle recovery and weight management. | |
| 5. Vegetable Juices | – Packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. |
| – Supports overall health and immune function. | |
| 6. Fruit Juices | – Provides natural sugars and essential nutrients. |
| – Hydrating and rich in vitamins. | |
| 7. Meal Replacement Drinks | – Balanced nutrition in a convenient form. |
| – Can support weight management goals. | |
| 8. Herbal Teas | – Hydrating and may have antioxidant properties. |
| – Some herbal teas can aid digestion. | |
| 9. Water-Based Smooth Soups | – Low-calorie option with hydration benefits. |
| – Contains a variety of vegetables for nutrients. | |
| 10. Yogurt Drinks | – Provides probiotics for gut health. |
| – Aids digestion and supports a healthy microbiome. |
A day’s menu might include Liquid Diet Foods
| Meal | Liquid Diet Foods | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Breakfast | Green Smoothie | – Spinach, banana, and protein powder blend for a nutrient-rich start. |
| Herbal Tea | – Hydration and potential digestive support. | |
| Mid-Morning Snack | Vegetable Juice | – Carrot, celery, and beet juice for vitamins and minerals. |
| Lunch | Tomato Basil Soup | – Low-calorie, hydrating, and rich in antioxidants. |
| Protein Shake | – Supports muscle health and adds protein to the meal. | |
| Afternoon Snack | Yogurt Smoothie | – Greek yogurt, berries, and honey for probiotics and antioxidants. |
| Dinner | Broccoli and Cheddar Soup | – Provides essential nutrients with a creamy texture. |
| Meal Replacement Drink | – Balanced nutrition with added vitamins and minerals. | |
| Evening Snack | Fruit Juice Popsicles | – Hydrating and a refreshing treat with natural sugars. |
Remember, this is just a sample menu, and individual dietary needs may vary. It’s crucial to ensure that the liquid diet is well-balanced, providing a variety of nutrients. Consulting with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian is advisable before embarking on a liquid diet or making significant changes to your eating habits.
Foods to avoid on a liquid diet
When following a liquid diet, certain foods are typically best avoided to ensure the diet’s effectiveness and prevent potential complications. Here’s a list of foods to generally avoid on a liquid diet:
- Solid Foods: The primary principle of a liquid diet is to avoid solid foods. This includes items like meats, grains, and other foods that require chewing.
- Highly Processed Foods: Foods high in processed sugars, artificial additives, and preservatives should be limited. Opt for whole, nutrient-dense liquids instead.
- Dairy Products (for some individuals): Some people may need to avoid dairy during a liquid diet, especially if they are lactose intolerant or have difficulty digesting dairy products.
- Fried Foods: Fried foods can be high in unhealthy fats and may be difficult to digest. Choose healthier cooking methods for any solid components of the diet.
- Sugary Beverages: Avoid sugary drinks like sodas, energy drinks, and sweetened juices. These can contribute to excessive calorie intake and may not provide essential nutrients.
- Alcohol: Alcohol can dehydrate the body and may not provide the necessary nutrients. It’s generally best to avoid alcoholic beverages during a liquid diet.
- Caffeinated Beverages (in excess): While moderate intake of caffeine is generally acceptable for many individuals, excessive caffeine consumption can contribute to dehydration.
- High-Fiber Foods: While some fiber is beneficial, too much fiber can be difficult to digest on a liquid diet. Limit foods like raw vegetables and whole grains.
- Spicy Foods: Spicy foods may irritate the digestive system, and their strong flavors can be overwhelming when consumed in liquid form.
- High-Calorie Liquid Snacks: Be cautious with liquid snacks that are high in calories without providing significant nutritional value. Opt for nutrient-dense options instead.
It’s essential to note that the specific foods to avoid can vary depending on the purpose and duration of the liquid diet, as well as individual health considerations. Before starting a liquid diet or making significant changes to your eating habits, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to ensure that the plan is appropriate for your specific needs and health status.
Things to think about before beginning a liquid diet
Before beginning a liquid diet, there are several important considerations to take into account. Here are key things to think about:
- Consultation with a Healthcare Professional: Always consult with your healthcare provider or a registered dietitian before starting a liquid diet, especially if you have pre-existing medical conditions, are taking medications, or have specific dietary requirements.
- Purpose of the Liquid Diet: Clearly define the purpose of the liquid diet. Whether it’s for weight loss, medical reasons, or a short-term cleanse, understanding your goals will help tailor the liquid diet to your needs.
- Duration of the Liquid Diet: Determine how long you plan to follow the liquid diet. Short-term liquid diets are often recommended for specific purposes, but long-term reliance on liquid nutrition may pose nutritional challenges.
- Nutritional Adequacy: Ensure that the liquid diet provides all the essential nutrients your body needs. This includes proteins, vitamins, minerals, and sufficient calories to support your energy levels and overall health.
- Variety in Liquid Options: Plan a diverse selection of liquids to avoid nutrient deficiencies and to make the diet more sustainable. Include a mix of smoothies, soups, broths, and other liquid-based meals.
- Hydration: Pay attention to hydration. While many liquid diet foods contribute to fluid intake, it’s essential to drink enough water throughout the day to stay adequately hydrated.
- Potential Side Effects: Be aware of potential side effects such as fatigue, dizziness, or digestive issues. If you experience any adverse effects, it’s important to reassess and consult with a healthcare professional.
- Medical Conditions and Medications: Consider how the liquid diet may interact with any existing medical conditions or medications you are taking. Certain conditions may require modifications to the liquid diet plan.
- Sustainability: Evaluate whether a liquid diet is sustainable for your lifestyle and preferences. Long-term adherence to a liquid diet can be challenging, and it’s important to have a plan for transitioning back to solid foods.
- Monitoring Progress: Establish a method for monitoring your progress. This could include regular check-ins with a healthcare professional, tracking weight loss or other health markers, and being attentive to how your body responds to the diet.
- Support System: Inform friends and family about your decision to follow a liquid diet and enlist their support. Having a support system can be crucial for motivation and encouragement.
Remember, individual responses to liquid diets can vary, and what works for one person may not be suitable for another. It’s crucial to approach any significant dietary changes with careful consideration and under the guidance of a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian.
Liquid Diet vs. Other Diets
| Aspect | Full Liquid Diet | Other Diets |
|---|---|---|
| Consistency of Foods | Liquid or semi-liquid form. | Solid foods in various textures. |
| Types of Foods Allowed | Liquids, soups, and certain beverages. | Varied, including solid foods. |
| Nutrient Density | Can be nutrient-dense with proper planning. | Nutrient density varies based on food choices. |
| Caloric Intake | Can be controlled for weight management. | Caloric intake varies by diet type. |
| Digestive Rest | Provides a rest for the digestive system. | Digestive demands depend on diet composition. |
| Duration | Short-term or medically prescribed. | Variable, ranging from short-term to long-term. |
| Weight Management | Can support weight loss if caloric intake is controlled. | Weight management goals vary by diet type. |
| Sustainability | Challenging for long-term adherence. | Sustainability depends on the diet’s structure. |
| Variety of Food Options | Limited compared to a regular diet. | Offers a wide range of food choices. |
| Medical Use | Prescribed for specific medical reasons or procedures. | May or may not have a medical focus. |
| Example Diets | Clear liquids, broths, and smoothies. | Mediterranean, Keto, Paleo, etc. |
| Potential Risks | Risk of nutrient deficiencies if not properly planned. | Risks vary based on diet type; nutrient imbalances, lack of variety, etc. |
| Consultation Requirement | Often requires consultation with a healthcare professional. | Consultation may vary depending on the diet and individual health. |
liquid diet for weight loss
A liquid diet for weight loss typically involves consuming liquids or foods that are in liquid form while controlling calorie intake. It’s important to note that any weight loss plan, including liquid diets, should be approached with caution, and it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian before making significant changes to your diet. Here’s a sample one-day liquid diet plan for weight loss:
Breakfast: Green Detox Smoothie
- Ingredients:
- 1 cup spinach
- 1/2 cucumber
- 1/2 green apple
- 1/2 lemon (juiced)
- 1/2 cup coconut water
- Ice cubes (optional)
- Instructions:
- Blend all ingredients until smooth.
- Add ice cubes if desired.
Mid-Morning Snack: Protein Shake
- Ingredients:
- 1 scoop protein powder (whey, pea, or plant-based)
- 1 cup unsweetened almond milk
- 1/2 banana
- Instructions:
- Blend all ingredients until well combined.
Lunch: Vegetable Broth with Quinoa
- Ingredients:
- 2 cups vegetable broth (low sodium)
- 1/4 cup quinoa, rinsed
- 1/2 cup finely chopped carrots and celery
- 1/4 cup chopped spinach
- Instructions:
- Bring vegetable broth to a simmer in a pot.
- Add quinoa, carrots, celery, and spinach.
- Cook until quinoa is tender.
Afternoon Snack: Greek Yogurt Smoothie
- Ingredients:
- 1/2 cup Greek yogurt
- 1/2 cup mixed berries (strawberries, blueberries)
- 1 tablespoon chia seeds
- Instructions:
- Blend all ingredients until smooth.
Dinner: Creamy Tomato Basil Soup
- Ingredients:
- 1 cup tomato juice (low sodium)
- 1/2 cup low-fat plain Greek yogurt
- 1/2 teaspoon olive oil
- Fresh basil leaves
- Salt and pepper to taste
- Instructions:
- Mix tomato juice, yogurt, olive oil, and basil in a blender.
- Blend until smooth.
- Warm the soup on the stove if desired.
Evening Snack: Herbal Tea with Lemon
- Ingredients:
- Herbal tea bag (chamomile, peppermint, or your choice)
- 1/2 lemon (sliced)
- Instructions:
- Brew herbal tea and add lemon slices for flavor.
liquid diet food recipes
Green Protein Smoothie
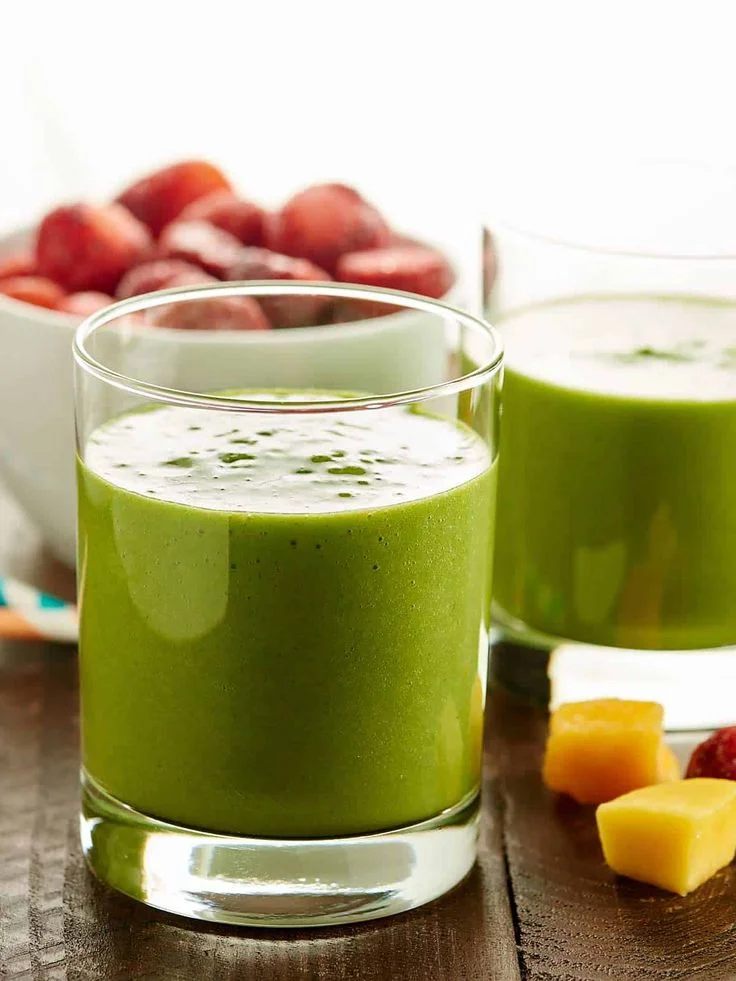

Ingredients:
- 1 cup spinach leaves
- 1/2 cucumber, peeled
- 1/2 banana
- 1/2 cup Greek yogurt
- 1/2 cup almond milk
- 1 tablespoon chia seeds
Instructions:
- Blend all the ingredients until smooth.
- Optionally, add ice for a refreshing texture.
Creamy Tomato Basil Soup
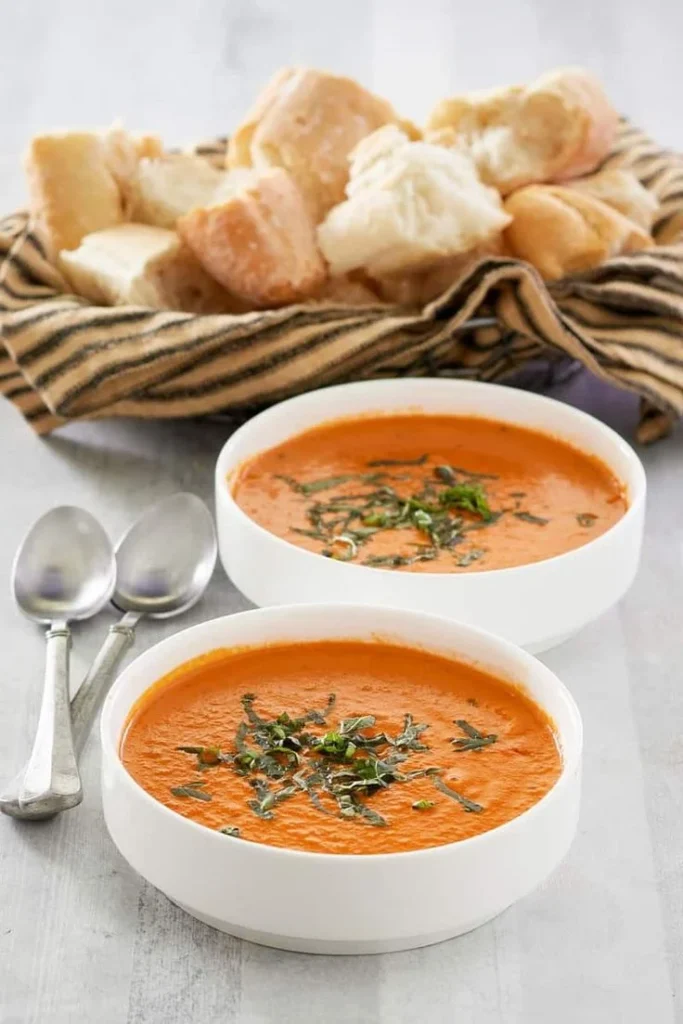

Ingredients:
- 1 cup tomato juice (low sodium)
- 1/2 cup low-fat plain Greek yogurt
- 1/2 teaspoon olive oil
- Fresh basil leaves
- Salt and pepper to taste
Instructions:
- Mix tomato juice, yogurt, olive oil, and basil in a blender.
- Blend until smooth.
- Season with salt and pepper.
- Warm the soup on the stove if desired.
Berry Protein Smoothie Bowl
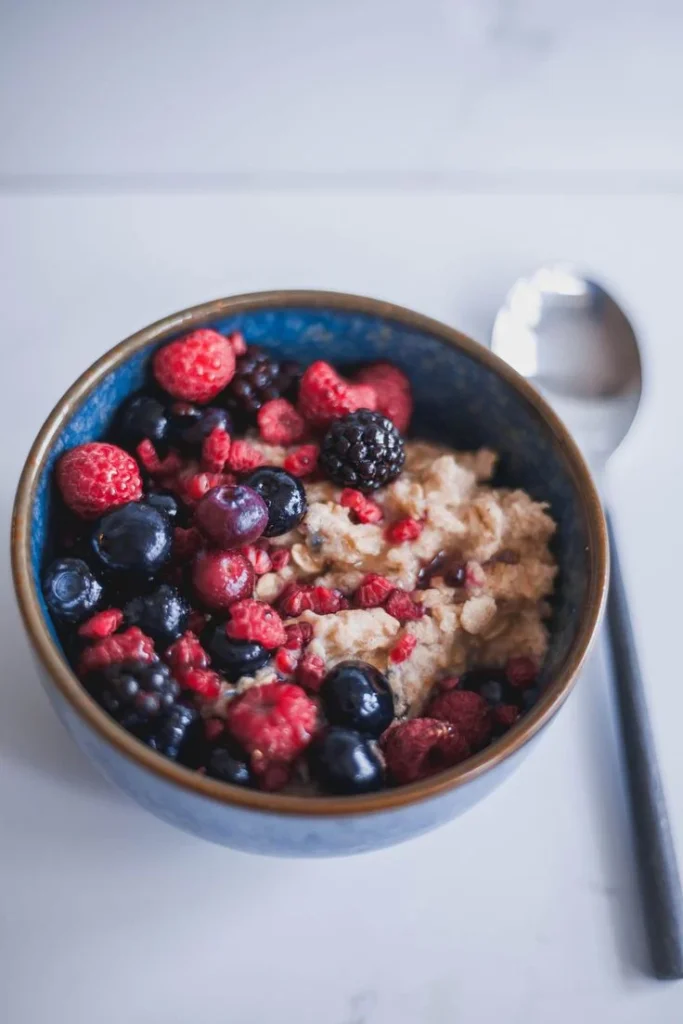

Ingredients:
- 1 cup mixed berries (strawberries, blueberries, raspberries)
- 1/2 cup almond milk
- 1/2 cup low-fat cottage cheese
- 1 tablespoon honey
- Granola and sliced almonds for topping
Instructions:
- Blend berries, almond milk, cottage cheese, and honey until smooth.
- Pour into a bowl and top with granola and sliced almonds.
Vegetable Broth with Quinoa
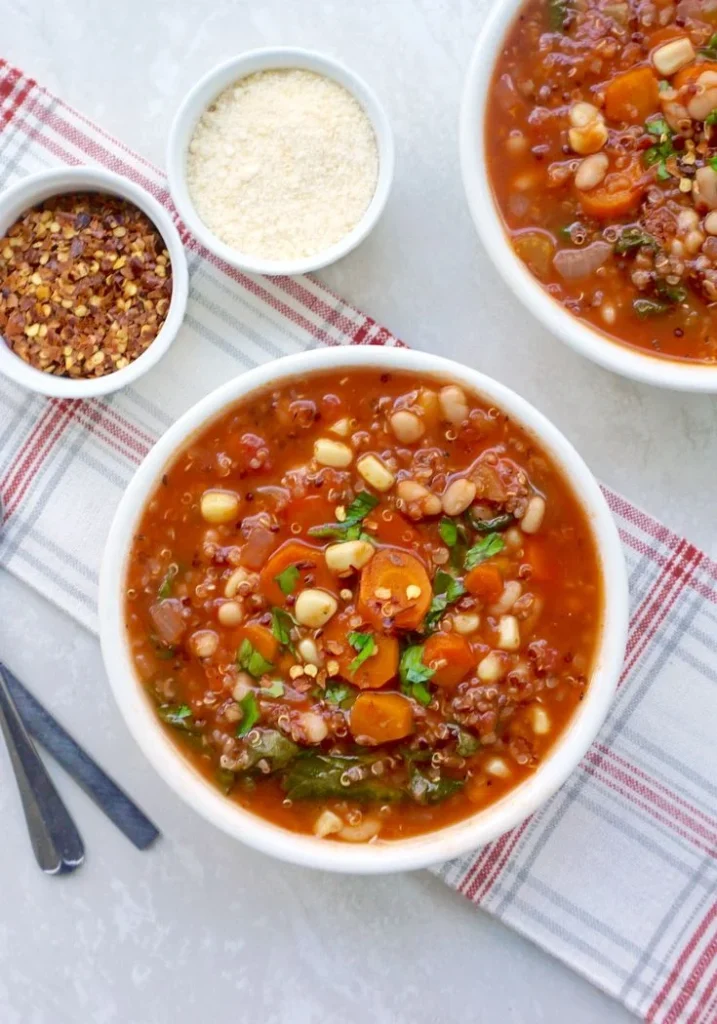

Ingredients:
- 2 cups vegetable broth (low sodium)
- 1/4 cup quinoa, rinsed
- 1/2 cup finely chopped carrots and celery
- 1/4 cup chopped spinach
- Salt and pepper to taste
Instructions:
- In a pot, bring vegetable broth to a simmer.
- Add quinoa, carrots, celery, and spinach.
- Cook until quinoa is tender.
- Season with salt and pepper.
Avocado and Banana Smoothie
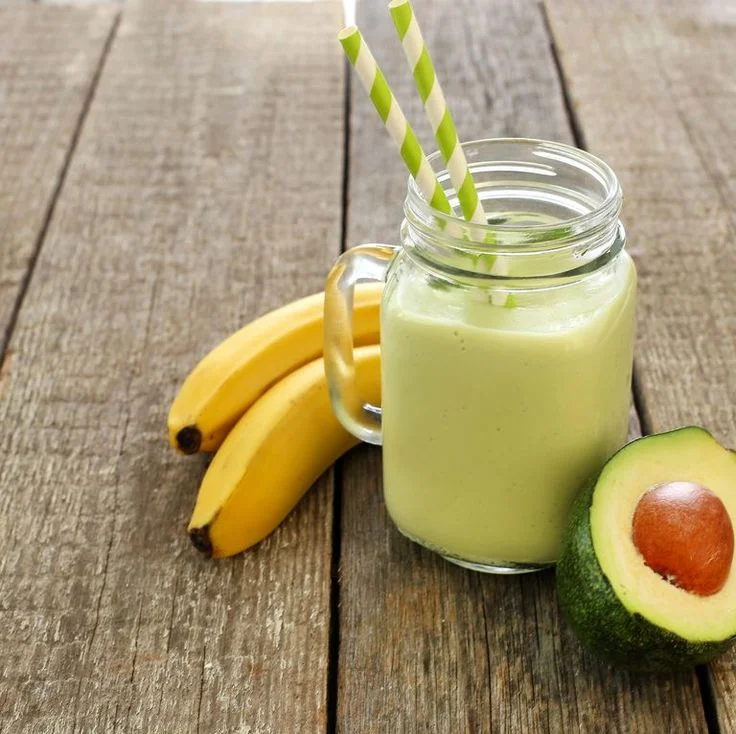

Ingredients:
- 1/2 avocado
- 1/2 banana
- 1 cup coconut water
- 1 tablespoon chia seeds
- Ice cubes
Instructions:
- Blend avocado, banana, coconut water, and chia seeds until creamy.
- Add ice cubes for a chilled consistency.
Summary
If an accident or disease is keeping you from chewing, swallowing, or digesting food easily, your doctor could recommend a whole liquid diet. To aid in your recovery following gastrointestinal surgery, it could also be advised.
Completely liquid diets are often followed for a few days to a week or longer. Constipation, diarrhea, weariness, and weight loss are among the side effects.
Work with your healthcare practitioner, a licensed dietitian, or a nutritionist who can assist you in creating a suitable food plan to better ensure that you achieve your nutritional needs.