Are you looking to build a strong and chiseled chest? Dumbbell chest exercises are a great way to target your upper body and achieve your fitness goals. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned gym-goer, mastering these exercises can help you take your upper body workout to the next level.
The chest is a key muscle group that many people strive to develop. Dumbbell exercises are effective in targeting the pectoral muscles and can help improve strength, muscle tone, and overall upper-body performance. However, performing these exercises with proper form and technique is crucial to maximize their benefits.
The muscles of the chest
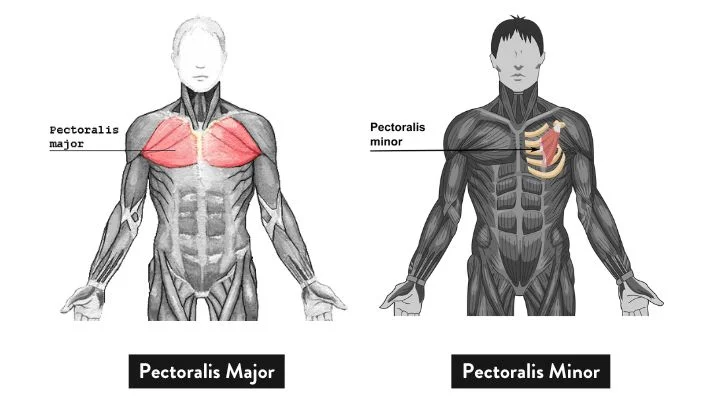
Located in the anterior (frontal) part of the upper torso, the pectoral muscles, also referred to as “pecs,” are a powerful collection of muscles. These muscles are important for a variety of functional activities involving the arms and shoulders in addition to looks. Now let’s examine the structure and purposes of the muscles in the chest:
- Pectoralis Major: The largest and most visible muscle in the chest is this one. It begins in the cartilage of the upper ribs, the clavicle, and the sternum before inserting into the humerus, the upper arm bone. The shoulder joint can move in several ways, including flexion, adduction, and medial rotation, thanks to the pectoralis major. Exercises like bench presses, push-ups, and chest fly heavily incorporate it.
- Pectoralis Minor: The smaller, triangular pectoralis minor muscle is situated beneath the pectoralis major. It attaches to the scapula’s coracoid process after emerging from the third, fourth, and fifth ribs (shoulder blade). The pectoralis minor, despite its small size, is an essential muscle for maintaining the shoulder blade and supporting actions like scapular protraction and downward rotation.
- Serratus Anterior: The serratus anterior is strongly related to the chest area even if it isn’t technically speaking a chest muscle. It inserts into the medial border of the scapula after emerging from the upper eight or nine ribs. For actions like pushing and punching, the serratus anterior is essential because it protracts the scapula, bringing it forward around the rib cage.
Together, these muscles may perform a variety of arm and shoulder motions, such as pushing, lifting, and stabilizing the upper body during exercise. In addition to improving upper body strength, strengthening the chest muscles also improves posture and general functional fitness.
Exercises like dumbbell flies, push-ups, cable crossovers, chest dips, and bench presses (flat, incline, or decline) are good for building the muscles in the chest. To promote healthy development and reduce the chance of overuse problems, it’s critical to include a range of exercises and resistance levels in your exercise regimen. Furthermore, to maximize the benefits of chest workouts while lowering the risk of injury, good form and technique are essential.
Benefits of Dumbbell Chest Exercises
Exercises with dumbbells for the chest provide several advantages that enhance general strength, muscle growth, and functional fitness. Here are a few of the main advantages:
- Increased Muscle Activation: Compared to barbell workouts, dumbbell chest exercises demand more stabilization from the muscles because each arm must independently regulate its weight. The arms, shoulders, and chest all experience greater muscular activity as a result of this enhanced stabilization.
- Improved Symmetry: Exercise with dumbbells helps correct any imbalances in strength between the left and right sides of the body by allowing each side to function independently. Better overall symmetry in chest development may result from this.
- Range of Motion: Compared to barbell workouts, dumbbell chest exercises frequently provide a wider range of motion. Better muscular stretch and activation as a result of this wider range of motion may encourage the development and flexibility of muscles.
- Versatility: There are many various ways to target the chest muscles with dumbbell exercises. Targeting different parts of the chest is made possible by variations like flyes and pullovers, as well as incline, decline, and flat dumbbell presses.
- Functional Strength: Dumbbell exercises for the chest often imitate pushing actions from everyday life, such as opening doors or moving objects. You may build functional strength through dumbbell training, which benefits both daily activities and athletic performance.
- Joint Health: Compared to fixed barbell workouts, dumbbell exercises allow for a more natural movement pattern, which might lessen stress on the joints. Those who have joint problems or want to avoid being hurt might benefit from this.
- Convenience: Exercises with dumbbells require little space and equipment, so they’re ideal for at-home workouts or situations where access to the gym is restricted. A pair of dumbbells is all you need to complete several efficient exercises for your chest.
- Progressive Overload: Because dumbbells come in different weights, it’s simple to advance your skills as you gain strength. Over time, you can continue to challenge your muscles and encourage muscle growth by progressively increasing the weight.
Dumbbell chest exercises can help you develop a strong, well-balanced chest, increase functional strength, and improve your overall performance and fitness. To prevent injury and get the best results, it’s crucial to employ the correct form and technique and to gradually increase the weight and intensity.
Best dumbbell chest exercises
1. Dumbbell Bench Press

- Muscles Targeted: Pectoralis Major, Anterior Deltoids, Triceps
- Sets and Reps: 3 sets of 8-12 reps
To perform the Dumbbell Bench Press:
- Lie flat on a bench with a dumbbell in each hand, held at chest level, palms facing away from you.
- Press the dumbbells upward until your arms are fully extended but not locked out.
- Slowly lower the dumbbells back down to chest level, keeping your elbows at a 90-degree angle or slightly below.
- Repeat for the desired number of repetitions.
Tips:
- Keep your back flat against the bench and your feet firmly planted on the ground.
- Engage your core muscles throughout the movement to maintain stability.
- Focus on a controlled motion, avoiding jerky movements or swinging the weights.
- Exhale as you push the dumbbells up and inhale as you lower them back down.
- Start with lighter weights to perfect your form before increasing resistance.
2. Dumbbell Flyes

- Muscles Targeted: Pectoralis Major (Sternal portion), Anterior Deltoids
- Sets and Reps: 3 sets of 10-15 reps
To perform Dumbbell Flyes:
- Lie flat on a bench with a dumbbell in each hand, palms facing each other, and arms extended above your chest.
- With a slight bend in your elbows, lower the dumbbells out to the sides in a wide arc until you feel a stretch in your chest.
- Keep your elbows in a fixed position throughout the movement, maintaining a slight bend.
- Once you feel the stretch, reverse the movement, squeezing your chest muscles to bring the dumbbells back to the starting position.
- Exhale as you bring the dumbbells together and inhale as you lower them back down.
- Repeat for the desired number of repetitions.
Tips:
- Use a weight that allows you to perform the exercise with proper form and control.
- Focus on feeling the stretch in your chest muscles throughout the movement.
- Keep your shoulders down and back, avoiding any shrugging or hunching.
- Avoid locking out your elbows at the top of the movement to prevent strain on the joints.
- Engage your core muscles to stabilize your body throughout the exercise.
3. Incline Dumbbell Bench Press
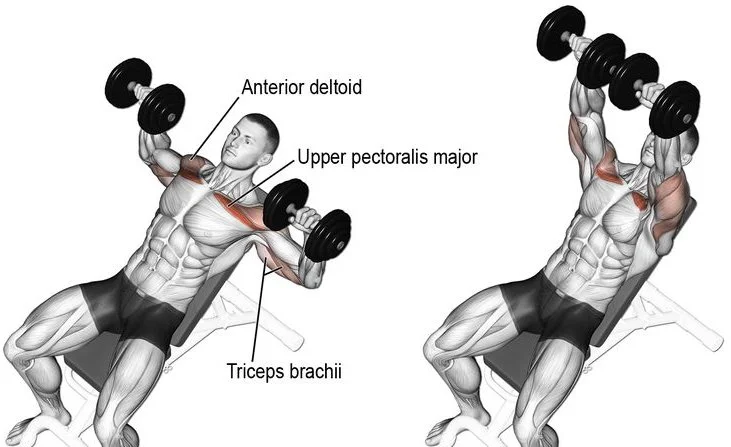
- Muscles Targeted: Upper Pectoralis Major, Anterior Deltoids, Triceps
- Sets and Reps: 3 sets of 8-12 reps
To perform the Incline Dumbbell Bench Press:
- Set an adjustable bench to an incline of around 30 to 45 degrees.
- Sit on the incline bench and hold a dumbbell in each hand at shoulder level, palms facing away from you.
- Press the dumbbells upward until your arms are fully extended but not locked out, keeping your elbows slightly bent.
- Lower the dumbbells down to shoulder level, allowing your elbows to come out to the sides in a controlled manner.
- Pause briefly at the bottom of the movement, feeling the stretch in your chest muscles.
- Press the dumbbells back up to the starting position, squeezing your chest muscles at the top.
- Exhale as you press the dumbbells up and inhale as you lower them down.
- Repeat for the desired number of repetitions.
Tips:
- Maintain a stable position on the incline bench with your feet firmly planted on the ground.
- Keep your back flat against the bench throughout the exercise.
- Focus on a smooth and controlled motion, avoiding any jerky movements.
- Use a weight that challenges you while allowing you to maintain proper form.
- Keep your wrists straight and aligned with your forearms to prevent strain.
- Engage your core muscles to stabilize your body and protect your lower back.
4. Incline Dumbbell Flyes

- Muscles Targeted: Upper Pectoralis Major (Clavicular portion), Anterior Deltoids
- Sets and Reps: 3 sets of 10-15 reps
To perform Incline Dumbbell Flyes:
- Set an adjustable bench to an incline of approximately 30 to 45 degrees.
- Sit on the incline bench and hold a dumbbell in each hand, palms facing each other, and arms extended above your chest.
- With a slight bend in your elbows, lower the dumbbells out to the sides in a wide arc until you feel a stretch in your chest.
- Keep your elbows in a fixed position throughout the movement, maintaining a slight bend.
- Once you feel the stretch, reverse the movement, squeezing your chest muscles to bring the dumbbells back to the starting position.
- Exhale as you bring the dumbbells together and inhale as you lower them back down.
- Repeat for the desired number of repetitions.
Tips:
- Ensure that your back is fully supported by the bench throughout the exercise.
- Keep your shoulders down and back, avoiding any shrugging or hunching.
- Use a weight that allows you to perform the exercise with proper form and control.
- Focus on feeling the stretch in your chest muscles throughout the movement.
- Engage your core muscles to stabilize your body and prevent arching your back.
- Avoid locking out your elbows at the top of the movement to maintain tension on the chest muscles.
5. Decline Dumbbell Bench Press
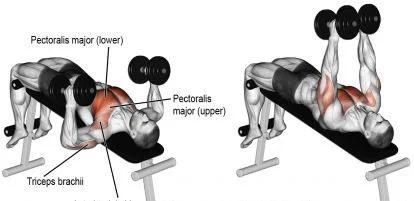
- Muscles Targeted: Lower Pectoralis Major, Triceps
- Sets and Reps: 3 sets of 8-12 reps
To perform the Decline Dumbbell Bench Press:
- Set up a decline bench at a slight angle, typically around 15 to 30 degrees declined.
- Lie back on the decline bench and hold a dumbbell in each hand at chest level, palms facing away from you.
- Keep your feet secure under the foot pads of the decline bench to stabilize your lower body.
- Press the dumbbells upward until your arms are fully extended but not locked out, keeping your elbows slightly bent.
- Lower the dumbbells down to chest level in a controlled manner, allowing your elbows to come out to the sides.
- Pause briefly at the bottom of the movement, feeling the stretch in your chest muscles.
- Press the dumbbells back up to the starting position, squeezing your chest muscles at the top.
- Exhale as you press the dumbbells up and inhale as you lower them down.
- Repeat for the desired number of repetitions.
Tips:
- Maintain a stable position on the decline bench with your back flat against the pad.
- Keep your shoulders down and back throughout the exercise to avoid strain.
- Use a weight that challenges you while allowing you to maintain proper form.
- Focus on a smooth and controlled motion, avoiding any jerky movements.
- Engage your core muscles to stabilize your body and protect your lower back.
- Keep your wrists straight and aligned with your forearms to prevent strain.
6. Decline Dumbbell Flyes
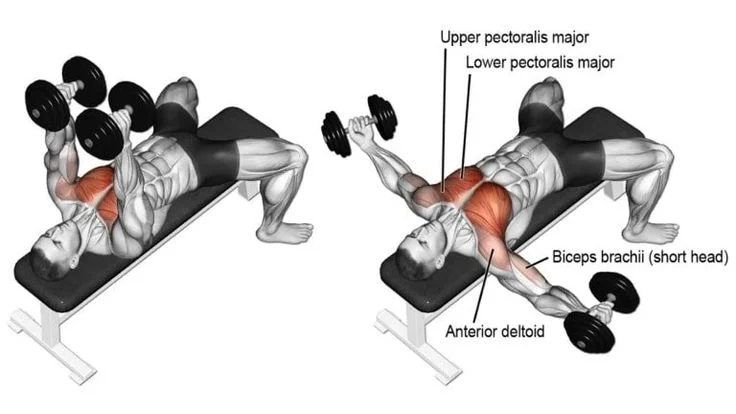
- Muscles Targeted: Lower Pectoralis Major, Anterior Deltoids
- Sets and Reps: 3 sets of 10-15 reps
To perform Decline Dumbbell Flyes:
- Set up a decline bench at a comfortable angle, typically around 15 to 30 degrees declined.
- Lie back on the decline bench with a dumbbell in each hand, palms facing each other, and arms extended above your chest.
- Maintain a slight bend in your elbows throughout the exercise.
- Lower the dumbbells out to the sides in a wide arc, keeping a slight bend in your elbows.
- Lower the dumbbells until you feel a stretch in your chest muscles, but avoid overextending or overstretching.
- Squeeze your chest muscles to bring the dumbbells back to the starting position, focusing on using your chest muscles to perform the movement.
- Exhale as you bring the dumbbells together and inhale as you lower them back down.
- Repeat for the desired number of repetitions.
Tips:
- Ensure that your back is fully supported by the decline bench throughout the exercise.
- Keep your shoulders down and back, avoiding any shrugging or hunching.
- Use a weight that allows you to perform the exercise with proper form and control.
- Focus on feeling the stretch in your chest muscles throughout the movement.
- Engage your core muscles to stabilize your body and prevent arching your back.
- Avoid locking out your elbows at the top of the movement to maintain tension on the chest muscles.
7. Dumbbell Pullover

- Muscles Targeted: Serratus Anterior, Pectoralis Major (Sternal portion), Latissimus Dorsi, Triceps
- Sets and Reps: 3 sets of 10-12 reps
To perform the Dumbbell Pullover:
- Lie flat on a bench with only your upper back and shoulders resting on the bench. Keep your feet flat on the floor and your knees bent at a 90-degree angle.
- Hold a single dumbbell with both hands, gripping one end of the dumbbell with both hands, palms pressing against the underside of the inner plate.
- Extend your arms straight above your chest, keeping a slight bend in your elbows. Your arms should be perpendicular to your body.
- Lower the dumbbell in an arc motion behind your head while keeping your elbows slightly bent.
- Feel a stretch in your chest and lats as you lower the dumbbell as far as comfortably possible.
- Slowly return the dumbbell to the starting position by reversing the motion, focusing on engaging your chest and lats.
- Keep your core engaged throughout the movement to stabilize your body.
- Exhale as you bring the dumbbell back up, and inhale as you lower it down.
- Repeat for the desired number of repetitions.
Tips:
- Use a moderate weight that allows you to maintain proper form and control throughout the exercise.
- Keep your hips stable and avoid arching your back excessively during the movement.
- Focus on feeling the stretch in your chest and lats as you lower the dumbbell behind your head.
- Control the motion throughout the exercise, avoiding any jerky movements.
- Keep your grip firm on the dumbbell to prevent it from slipping out of your hands.
8. Dumbbell Squeeze Press
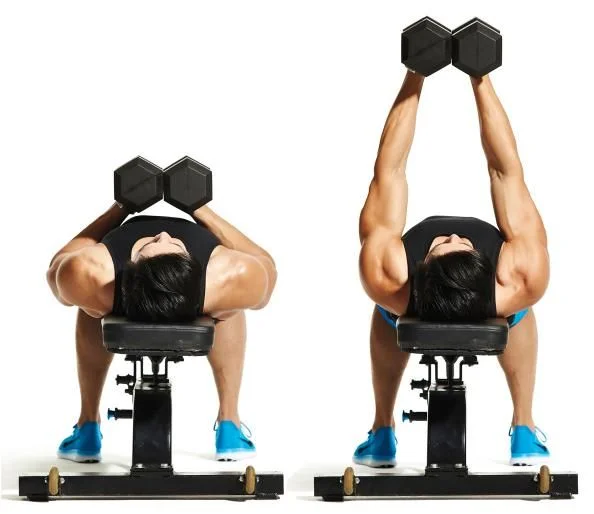

- Muscles Targeted: Pectoralis Major, Anterior Deltoids, Triceps
- Sets and Reps: 3 sets of 10-12 reps
To perform Dumbbell Squeeze Press:
- Lie flat on a bench with a dumbbell in each hand, held directly above your chest. Your palms should be facing each other, and your arms should be fully extended.
- Press the dumbbells together as hard as you can, engaging your chest muscles.
- Maintain this squeeze throughout the entire exercise.
- Slowly lower the dumbbells towards your chest while keeping them pressed together.
- Pause for a moment when the dumbbells are close to your chest, feeling the stretch in your chest muscles.
- Press the dumbbells back up to the starting position while continuing to squeeze them together.
- Repeat for the desired number of repetitions.
Tips:
- Focus on squeezing the dumbbells together throughout the entire movement to maximize chest engagement.
- Keep your elbows slightly bent throughout the exercise to reduce strain on the joints.
- Use a weight that allows you to maintain proper form and control while still challenging your chest muscles.
- Exhale as you press the dumbbells up and inhale as you lower them down.
- Keep your shoulder blades retracted and your back flat against the bench for stability.
- Avoid arching your back or lifting your hips off the bench during the exercise.
9. Dumbbell Hex Press

- Muscles Targeted: Pectoralis Major, Triceps
- Sets and Reps: 3 sets of 8-12 reps
To perform Dumbbell Hex Press:
- Lie flat on your back on the floor or on a bench with your knees bent and feet flat on the ground.
- Hold a dumbbell in each hand with an overhand grip, palms facing inward towards each other, and elbows bent at a 90-degree angle.
- Position the dumbbells directly above your chest, with your upper arms resting on the floor or bench.
- Press the dumbbells upward until your arms are fully extended, but do not lock out your elbows.
- Squeeze your chest muscles at the top of the movement, then slowly lower the dumbbells back down to the starting position, maintaining control.
- Keep your shoulder blades retracted and your core engaged throughout the exercise to stabilize your body.
- Repeat for the desired number of repetitions.
Tips:
- Use a weight that allows you to maintain proper form and control throughout the exercise.
- Focus on keeping your elbows at a 90-degree angle throughout the movement to effectively target the chest muscles.
- Keep your wrists straight and aligned with your forearms to prevent strain.
- Exhale as you press the dumbbells up and inhale as you lower them back down.
- Ensure your back remains flat against the floor or bench to avoid arching.
- Avoid bouncing the weights off your chest and maintain a smooth, controlled motion for maximum effectiveness and safety.
10. Single-Arm Dumbbell Bench Press
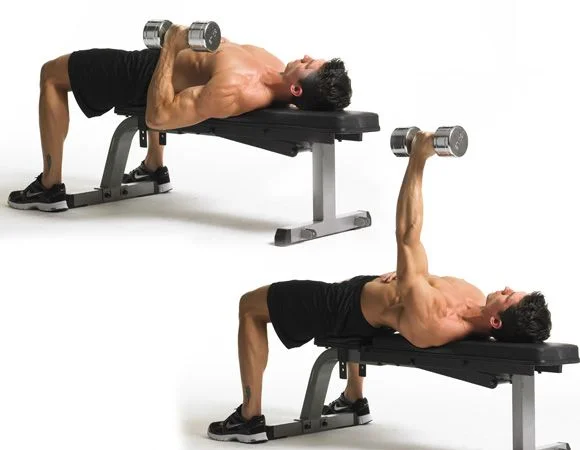

- Muscles Targeted: Pectoralis Major, Anterior Deltoids, Triceps, Core (for stability)
- Sets and Reps: 3 sets of 8-12 reps per arm
To perform the Single-Arm Dumbbell Bench Press:
- Lie flat on a bench with your feet planted firmly on the ground for stability. Hold a dumbbell in one hand, with your palm facing away from you, and extend your arm straight up towards the ceiling.
- Engage your core muscles to stabilize your body and maintain a neutral spine throughout the exercise.
- Lower the dumbbell slowly towards your chest while keeping your elbow tucked in close to your body. Aim to bring your upper arm parallel to the floor or slightly lower.
- Pause briefly when your elbow reaches about 90 degrees or when the dumbbell is close to your chest.
- Press the dumbbell back up to the starting position, fully extending your arm without locking out your elbow.
- Keep your shoulders and hips square throughout the movement, avoiding any rotation or twisting.
- Complete the desired number of repetitions on one side before switching to the other side.
Tips:
- Use a weight that allows you to maintain proper form and control throughout the exercise.
- Keep your wrist straight and aligned with your forearm to prevent strain.
- Focus on keeping your chest lifted and your shoulder blades retracted throughout the movement.
- Exhale as you press the dumbbell up and inhale as you lower it down.
- Maintain a slow and controlled pace to maximize muscle engagement and prevent injury.
- If you find it challenging to stabilize your body, start with a lighter weight or perform the exercise on a flat bench before progressing to an incline bench.