Enhance your nutrient intake with these zinc-rich fruits! Learn about the benefits of adding these delicious options to your daily meals.
Are you looking to boost your zinc intake through natural sources? Zinc is an essential micronutrient that plays a vital role in various bodily functions, including immune system support, wound healing, and DNA synthesis. While zinc supplements are available, getting this nutrient from whole foods is always a better option.
Potential Health Benefits of Zinc
As we previously observed, several potential health benefits are associated with adequate zinc levels. We have gone into great depth about these advantages here.
Immune System Support
Because zinc can help develop and activate T-cells, which protect your body from infections and disorders, zinc is essential for a robust immune system. A high zinc diet prevents sickness and expedites the healing process when it does occur.
Enhancing Metabolism
It is said that zinc is essential for numerous enzymatic functions that support a normal metabolism. Zinc helps to keep everything functioning properly by aiding in the breakdown of nutrients and the creation of proteins and DNA.
Skin Health
Consuming a lot of zinc may contribute to good skin. It aids in the regulation of skin oil production and is necessary for the synthesis of collagen. Better skin overall and fewer breakouts of acne may result from this.
Wound Repair
Wound healing is claimed to be greatly aided by zinc. Zinc is necessary for healthy mucosal and skin membranes as well as appropriate cell growth and development. This facilitates faster healing from cuts, burns, and scratches.
Zinc-Rich Fruits
Including fruits high in zinc in your diet can have a major positive impact on your general health and well-being. Zinc is an important mineral that is required for many body processes, such as cell division, wound healing, and immunological support. Incorporating naturally high-zinc fruits into your diet can help you reach your daily goals and maintain good health.
Here are some zinc-rich fruits, along with their approximate zinc concentration per 100 grams:
| Fruit | Zinc per 100 gm |
|---|---|
| Avocado | 0.64 mg |
| Guava | 0.23 mg |
| Blackberries | 0.53 mg |
| Raspberries | 0.42 mg |
| Pomegranate | 0.35 mg |
| Kiwi | 0.17 mg |
| Prunes | 0.44 mg |
| Dates | 0.29 mg |
1. Avocado
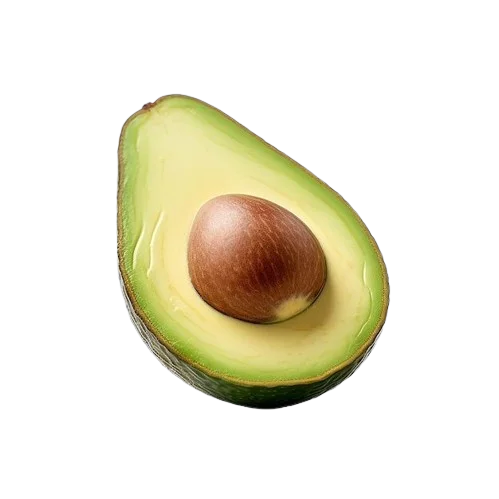

In addition to being a tasty fruit, avocados are a wonderful source of zinc. Avocados can help you meet your daily zinc requirement because they contain about 0.64 milligrams of zinc per 100 grams. Furthermore, avocados are a nutrient-dense option for any meal or snack because they are full of fiber, healthy fats, and a variety of vitamins and minerals.
2. Guava

Another fruit that is high in zinc is the guava, which has 0.23 milligrams of zinc per 100 grams. In addition to being tasty, this tropical fruit is also a great source of fiber, antioxidants, and vitamin C. Guava is a fruit that can strengthen your immune system and improve your general health.
3. Blackberries

Zinc content in blackberries is high, at 0.53 milligrams per 100 grams. These plump berries are a wonderful addition to your diet for encouraging good skin, enhancing immunity, and supporting digestive health because they are also a fantastic source of vitamin C, vitamin K, and antioxidants.
4. Raspberries

For every 100 grams, raspberries provide about 0.42 milligrams of zinc. These colorful berries are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals but low in calories. Raspberries are a nutrient-dense food that helps improve digestion, control blood sugar, and supply vital elements like zinc.
5. Pomegranate

The zinc content in pomegranate seeds is approximately 0.35 mg/100 grams. Pomegranates are well-known for their antioxidant qualities and possible health advantages, such as lowering inflammation, strengthening the heart, and fending against certain illnesses. Pomegranates can improve your diet and zinc consumption whether eaten as a snack or added to salads and smoothies.
6. Kiwi

The zinc content of kiwi fruit is about 0.17 mg/100 grams. Kiwis are high in dietary fiber, vitamin C, and vitamin K in addition to zinc. Regular kiwi consumption may boost immunity, facilitate digestion, and improve skin health.
7. Prunes

Zinc content in prunes, or dried plums, is approximately 0.44 mg/100 grams. Because of their high fiber content, prunes are widely known for their digestive advantages. They also supply vital minerals and vitamins, including antioxidants, potassium, and vitamin K.
8. Dates

Dates contain around 0.29 milligrams of zinc per 100 grams. These naturally sweet fruits are high in energy and include numerous elements such as fiber, potassium, and antioxidants. Dates can provide several health benefits, such as improved digestion, increased energy, and general well-being.
Including a variety of zinc-rich fruits in your diet will help you satisfy your daily zinc requirements while also promoting overall health and vigor. Add these fruits to your meals, snacks, or smoothies for a tasty and nutritious way to increase your zinc consumption.
What are the signs of low zinc in the body?
Zinc Deficiency
To maintain good health, it is critical to detect and treat zinc deficits. A lack of zinc can lead to a variety of health issues.
Symptoms of Zinc Deficiency
The following are some warning indications that you may be zinc deficient.
- Changes in flavor and scent
- Loss of appetite
- Diarrhea
- Hair loss
- Poor reaction to germs
- Impotence
- Stunted growth
Causes of Zinc Deficiency
The following factors may contribute to a zinc shortage.
- Not getting enough zinc from your food
- Not getting enough zinc (if you have gastrointestinal troubles)
- Needing additional zinc (during growth spurts or pregnancy).
- Chronic diseases include renal disease, diabetes, and liver disease.
- Drinking a lot of alcohol for a long time.
Summary
Consuming a balanced, nutrient-rich diet that includes enough zinc is essential for overall health and energy. While zinc-rich foods differ significantly, they all serve an important role in how our bodies function well. So, whether you avoid meat or eat everything, remember the importance of zinc, expand your diet to include zinc-rich foods, and get all of the potential advantages of this magnificent mineral.
FAQs
What food has the most zinc?
What fruits and vegetables are high in zinc?
How much zinc should I consume daily?
What happens when I over-consume zinc-rich foods?
How can I increase my zinc levels?
What foods cause a zinc deficiency?
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational/awareness purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for medical treatment by a healthcare professional and should not be relied upon to diagnose or treat any medical condition. The reader should consult a registered medical practitioner to determine the appropriateness of the information before consuming any medication. PharmEasy does not provide any guarantee or warranty (express or implied) regarding the accuracy, adequacy, completeness, legality, reliability, or usefulness of the information; and disclaims any liability arising thereof.
References
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Zinc Signals and Immunity [Internet]. [cited 2024 Jan 10]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5666901
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Zinc is an Essential Element for Male Fertility: A Review of Zn Roles in Men’s Health, Germination, Sperm Quality, and Fertilization [Internet]. [cited 2024 Jan 10]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6010824
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Zinc [Internet]. [cited 2024 Jan 10]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547698
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Zinc Deficiency [Internet]. [cited 2024 Jan 10]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK493231
- PubMed. Zinc Supplementation Reduces Common Cold Duration among Healthy Adults: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials with Micronutrients Supplementation [Internet]. [cited 2024 Jan 10]. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32342851
- PubMed. The effects of combined magnesium and zinc supplementation on metabolic status in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and coronary heart disease [Internet]. [cited 2024 Jan 10]. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32466773